Android and HashMap/Hashtable (Java) |
Android and HashMap/Hashtable (Java) สำหรับ HashMap และ Hashtable บนภาษา Java จะเป็น Collection ที่จะได้ใช้งานกันบ่อย ๆ เพราะเป็นรูปแบบการจัดเก็บค่าตัวแปร ที่อยู่ในรูปแบบของ Key และ Value ซึ่งจะแตกต่างกับ ArrayList ที่จะมีเพียงแค่ Index ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นทั้ง Key และ Value ใน Collection ของ HashMap และ Hashtable สามารถเพิ่มสมาชิกได้ไม่จำกัดนำนวน และไม่ต้องทราบถึงจำนวนขนาดหรือ Size สมาชิกล่วงหน้า คือสามารถเพิ่มได้เรื่อย ๆ จนเพียงพอแต่ความต้องการใช้งาน แต่การจัดเก็บจนมาเกินไปก็จะมีผลต่อ memory และความเร็วในการทำงานเช่นเดียวกัน เพราะฉะนั้นการใช้ตัวแปรเหล่านี้จะต้องใช้ให้เหมาะสม ยิ่งเมื่อต้องการจัดเก็บข้อมูลประเภท Object , Byte หรือพวก Bitmap ก็จะต้องใช้ memory จำนวนมากในการจัดเก็บเช่นเดียวกัน แต่ถ้าเป็นข้อมูลประเภท String หรือ Int(Number) จะสามารถเก็บได้ในประมาณมาก สำหรับรูปแบบการทำงานของ HashMap และ Hashtable นั้นจะคล้ายกันเกือบถึง 95% คือมีรูปแบบ และ method ที่เหมือน ๆ กับ แต่จะมีข้อแตกต่างกันอยู่ 2-3 ชุด เช่น
HashMap จะยอมให้มีค่าว่าง (null) เป็นทั้ง Key และ Value และ HashMap จะเป็นประเภท unsynchronized
Hashtable จะไม่ยอมให้มีค่าว่าง (null) ที่เป็น Key หรือ Value และจะเป็นประเภท synchronized
ความแตกต่างระหว่า unsynchronized กับ synchronized คือ รูปแบบ unsynchronized จะสามารถเข้าใช้งาน Collection นั้น ๆ ได้พร้อมกันหลาย ๆ Thread พร้อมกัน เฉพาะฉะนั้นจะสามารถทำงานเร็วกกว่า เหมาะกับข้อมูลที่ไม่ต้องการเปลี่ยนแปลง เพระาถ้ามีการเปลี่ยนแปลงข้อมูลเกิดขึ้นก่อนที่จะทำการ Update ไปยัง Collection การทำงานของ Thread อื่น ๆ ที่กำลังทำอยู่ในขณะเดียวกัน ก็อาจจะได้ข้อมูลที่ไม่ค่อยถูกต้อง ส่วน synchronized เป็นรูปแบบการทำงานที่จะ Lock Collection ที่ถูกเรียกใช้งานอยู่และ Thread ที่จะเข้ามาใช้งานต่อจากนั้นจะต้องรอคิวจนกว่า Thread แรกได้ทำงานเสร็จสิ้นไปแล้ว ซึ่งจะเหมาะกับชุดของข้อมูล ที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบ่อยและต้องการความถูกต้องแม่นย้ำสูง แต่ข้อเสียคือการทำงานก็จะช้าลงไปด้วย
เพระาฉะนั้นการเลือกใช้งานระหว่าง HashMap และ Hashtable จะต้องเลือกใช้ให้เหมาะสมกับประเภทของชุดข้อมูลด้วย แต่ในหลักการเขียนโปรแกรมทั่ว ๆ ไป HashMap จะเป็นทางเลือกในใช้งานผ่าน Collection ประเภทนี้ซะมากว่า ส่วนเหตุผลได้อธิบายจากความแตกต่างระหว่าง unsynchronized กับ synchronized
(ผิดพลาดประการใดต้องขออภัยมา ณ ที่นี้ด้วยครับ)
ตัวอย่างการใช้ HashMap และ Hashtable
- HashMap
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("MemberID", "1");
map.put("Name", "Weerachai");
map.put("Tel", "0819876107");
ตัวอย่างการประกาศตัวแปรแบบ HashMap ซึ่งมี Key และ Value อยู่ 3 รายการ
- HashMap
Hashtable<String,String> table = new Hashtable<String,String>();
table = new Hashtable<String, String>();
table.put("MemberID", "2");
table.put("Name", "Win");
table.put("Tel", "021978032");
ตัวอย่างการประกาศตัวแปรแบบ Hashtable ซึ่งมี Key และ Value อยู่ 3 รายการ
ตัวอย่างนับขนาดหรือ Size ของ HashMap และ Hashtable
map.size();
table();
ตัวอย่าง Loop ค่าของ HashMap และ Hashtable
- HashMap
Iterator<String> Vmap = map.keySet().iterator();
while(Vmap.hasNext()){
String key = (String)(Vmap.next()); // Key
String val = map.get(key); // Value
//txtView2.setText(txtView2.getText() + key + "=" + val + ",\r\n");
}
map.clear();
- Hashtable
Iterator<String> Vtable = table.keySet().iterator();
while(Vtable.hasNext()){
String key = (String)(Vtable.next()); // Key
String val = table.get(key); // Value
//txtView4.setText(txtView4.getText() + key + "=" + val + ",\r\n");
}
table.clear();
ตัวอย่างการอ้างถึงตำแหน่งของ HashMap และ Hashtable
map.containsKey("MemberID"); // result = 1
table.containsKey("MemberID"); // result = 2
map.containsValue("0819876107"); // result = Tel
table.containsValue("021978032"); // result = Tel
Example 1 การใช้ HashMap กับ Hashtable เพื่อจัดเก็บและแสดงผลข้อมูลต่าง ๆ
ออกแบบ XML Layout

activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="22dp"
android:text="TextView" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="TextView" />
</RelativeLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.myapp;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/**** Sample HashMap ****/
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("MemberID", "1");
map.put("Name", "Weerachai");
map.put("Tel", "0819876107");
// Get Size HashMap
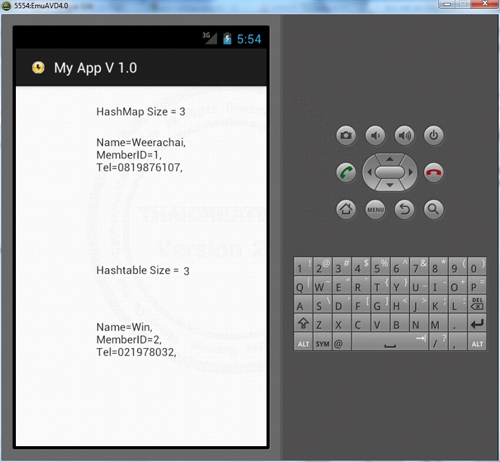
final TextView txtView1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
txtView1.setText("HashMap Size = " + map.size());
// Loop Data HashMap
final TextView txtView2 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView2);
txtView2.setText("");
Iterator<String> Vmap = map.keySet().iterator();
while(Vmap.hasNext()){
String key = (String)(Vmap.next()); // Key
String val = map.get(key); // Value
txtView2.setText(txtView2.getText() + key + "=" + val + ",\r\n");
}
map.clear();
/**** Sample Hashtable ****/
Hashtable<String,String> table = new Hashtable<String,String>();
table = new Hashtable<String, String>();
table.put("MemberID", "2");
table.put("Name", "Win");
table.put("Tel", "021978032");
// Get Size Hashtable
final TextView txtView3 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView3);
txtView3.setText("Hashtable Size = " + table.size());
// Loop Data Hashtable
final TextView txtView4 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView4);
txtView4.setText("");
Iterator<String> Vtable = table.keySet().iterator();
while(Vtable.hasNext()){
String key = (String)(Vtable.next()); // Key
String val = table.get(key); // Value
txtView4.setText(txtView4.getText() + key + "=" + val + ",\r\n");
}
table.clear();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Screenshot
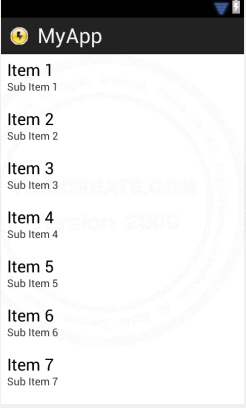
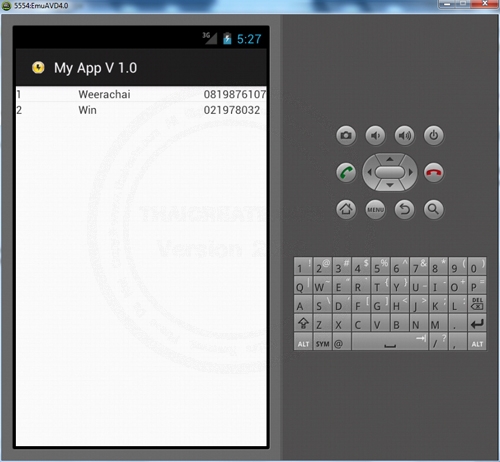
Example 2 การใช้งาน HashMap ร่วมกับ ArrayList เพื่อจัดเก็บข้อมูลที่มี Key และ Value แต่หลาย Index
ออกแบบ XML Layout
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.1">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>

activity_column.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/ColMemberID"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="MemberID"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/ColName"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="Name"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/ColTel"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Tel" />
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.myapp;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// listView1
final ListView lisView1 = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.listView1);
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> MyArrList = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
HashMap<String, String> map;
/*** Rows 1 ***/
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("MemberID", "1");
map.put("Name", "Weerachai");
map.put("Tel", "0819876107");
MyArrList.add(map);
/*** Rows 2 ***/
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("MemberID", "2");
map.put("Name", "Win");
map.put("Tel", "021978032");
MyArrList.add(map);
SimpleAdapter sAdap;
sAdap = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, MyArrList, R.layout.activity_column,
new String[] {"MemberID", "Name", "Tel"}, new int[] {R.id.ColMemberID, R.id.ColName, R.id.ColTel});
lisView1.setAdapter(sAdap);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Screenshot
| Property & Method (Others Related) |
|
 ช่วยกันสนับสนุนรักษาเว็บไซต์ความรู้แห่งนี้ไว้ด้วยการสนับสนุน Source Code 2.0 ของทีมงานไทยครีเอท ช่วยกันสนับสนุนรักษาเว็บไซต์ความรู้แห่งนี้ไว้ด้วยการสนับสนุน Source Code 2.0 ของทีมงานไทยครีเอท
|
|
| |
By : |
ThaiCreate.Com Team (บทความเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของเว็บไทยครีเอทห้ามนำเผยแพร่ ณ เว็บไซต์อื่น ๆ) |
| |
Score Rating : |
    |
|
| |
Create/Update Date : |
2012-07-29 17:46:16 /
2012-07-30 10:54:10 |
| |
Download : |
No files |
|
|
Sponsored Links / Related |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|